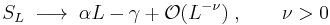Topological entropy in physics
The topological entanglement entropy, usually denoted by γ, is a number characterizing many-body states that possess topological order. The short form topological entropy is often used, although the same name in ergodic theory refers to an unrelated mathematical concept (see topological entropy).
A non-zero topological entanglement entropy reflects the presence of long range quantum entanglements in a many-body quantum state. So the topological entanglement entropy links topological order with pattern of long range quantum entanglements.
Given a topologically ordered state, the topological entropy can be extracted from the asymptotic behavior of the Von Neumann entropy measuring the quantum entanglement between a spatial block and the rest of the system. The entanglement entropy of a simply connected region of boundary length L, within an infinite two-dimensional topologically ordered state, has the following form for large L:
-γ is the topological entanglement entropy.
The topological entanglement entropy is equal to the logarithm of the total quantum dimension of the quasiparticle excitations of the state.
For example, the simplest fractional quantum Hall states, the Laughlin states at filling fraction 1/m, have γ = ½log(m). The Z2 fractionalized states, such as topologically ordered states of Z2 spin-liquid, quantum dimer models on non-bipartite lattices, and Kitaev's toric code state, are characterized γ = log(2).
Contents |
See also
- Quantum topology
- Topological defect
- Topological order
- Topological quantum field theory
- Topological quantum number
- Topological string theory
References
Introduction of the quantity
- Topological Entanglement Entropy, Alexei Kitaev and John Preskill, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 110404 (2006).
- Detecting Topological Order in a Ground State Wave Function, Michael Levin and Xiao-Gang Wen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 110405 (2006).
Calculations for specific topologically ordered states
- M. Haque, O. Zozulya and K. Schoutens; Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 060401 (2007).
- S. Furukawa and G. Misguich, Phys. Rev. B 75, 214407 (2007).